What Is An ETF and Should You Invest?
ETF’s are a great way to get into investing. They are also a great option to diversify your portfolio. If you want to own a bunch of stocks but cannot afford to do so, an ETF is perfect for you. ETF’s combine many different companies under one umbrella and some even pay you to hold them. This is great for dividend investing. I myself own a couple ETFs, QYLD and JEPQ are the two I own. I am very happy with these two.
What Is an ETF?
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have gained significant popularity among investors in recent years. However, what exactly is an ETF, and how does it differ from other investment options? In this article, we will explore the concept of ETFs, their benefits, and how they work.
Understanding ETFs
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product that allows investors to buy and sell shares representing ownership in a diversified portfolio of assets. These assets can include stocks, bonds, commodities, or a mix of various asset classes. For example, let us examine QYLD and its top ten holdings.
| Company Symbol | Company Name | Holdings Percentage |
| AAPL | Apple Inc | 11.84% |
| MSFT | Microsoft Corp | 9.57% |
| AMZN | Amazon.com Inc | 5.25% |
| NVDA | NVIDIA Corp | 4.42% |
| META | Meta Platforms Inc Class A | 3.78% |
| TSLA | Tesla Inc | 3.25% |
| AVGO | Broadcom Inc | 3.08% |
| GOOGL | Alphabet Inc Class A | 3.02% |
| GOOG | Alphabet Inc Class C | 2.99% |
| Ndx Us 08/18/23 C15475 | 2.73% |
You can see here that this ETF has many different companies under its name. This allows you to have a piece of all these companies and make money doing so. QYLD currently gives out 8.59% for its dividend yield and its current share price is $17.78 which makes it an affordable ETF.
How do ETFs work?
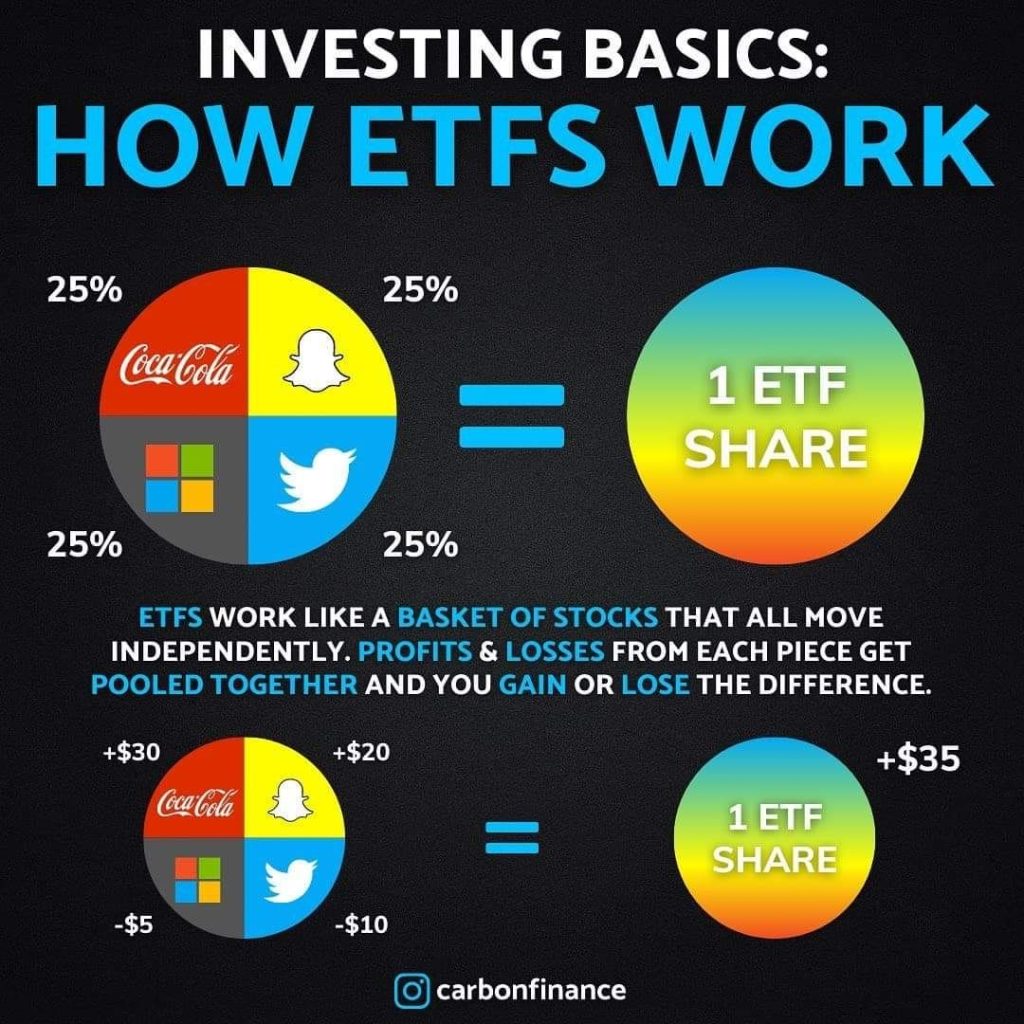
ETFs are designed to track the performance of a specific index, sector, or asset class. Think of them as baskets of assets that mimic the index they are designed to replicate. For example, an ETF tracking the S&P 500 index will hold the same stocks in the same proportion as the index.
Unlike mutual funds, which are priced once a day after the market closes, ETFs trade like a stock throughout the day. This means that their prices fluctuate based on supply and demand, just like individual stocks.
The Benefits of ETFs
ETFs offer several advantages that have contributed to their popularity:
- Diversification – By investing in an ETF, investors gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of assets. This diversification helps reduce the risk associated with investing in a single stock.
- Lower Costs -Compared to mutual funds, ETFs generally have lower expense ratios. This is because ETFs are passively managed and aim to replicate the performance of an index, rather than actively selecting and managing individual securities.
- Liquidity – Since ETFs trade on stock exchanges, they offer high liquidity. Investors can buy or sell shares at any time during market hours, providing flexibility and ease of access to their investments.
- Transparency – ETFs disclose their holdings on a daily basis, allowing investors to know exactly what assets are included in the fund. This transparency provides investors with a clear understanding of their investment.
Conclusion
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have revolutionized the way investors approach diversification and access to various asset classes. With their unique structure and benefits, ETFs have become a favored investment option for many. By providing diversification, lower costs, liquidity, and transparency, ETFs offer investors a convenient and efficient way to gain exposure to a wide range of assets.
